The measurement of Cell-based Molecular Bioactivity (CMB) is critical for almost every step of drug development, such as: target identification/validation, lead identification/optimization, and toxicology screenings. In particular, the CMBs are more representative of human physiology than that for purified targets in linking to disease of interest during target identification/validation; correlate binding parameter with phenotypic outcome in analyzing cellular structure-activity relationships during lead identification/optimization; facilitate toxicology screenings of drugs by identifying off-target in the native cellular contexts. All the analyses highlight the demands for the invaluable information of Cell-based Molecular Bioactivities (CMBs). With the booming applications of AI in biomedicine, it is also imperative to have a CMB-based database facilitating the learning of cell-based molecular patterns for guiding modern drug discovery.
MolBiC: a Cell-based Landscape Illustrating Molecular Bioactivities, was therefore constructed to provide the valuable data of molecular bioactivity measured within the cellular contexts. First, such data were accumulated by searching such keywords as ' intracellular binding assay ', 'cellular activity' and 'intracellular target binding' in PubMed, which led to over 550,000 experiment-validated CMBs between 321,086 compounds and 2,666 targets within the context of 988 cell lines. Second, those CMBs were comprehensively collected to our database and quantitatively classified according to their activities, which resulted in 188,027, 177,755 and 73,246 data of high (≤100 nM), medium (between 100 nM and 10 μM), and low (>10 μM) CMBs, respectively. Finally, a total of 114 disease classes defined by the WHO ICD-11 (such as Alzheimer disease, lung cancer, diabetes mellitus, influenza, follicular lymphoma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), 155 biochemical classes of targets (such as cytochrome P450, neurotransmitter receptor, protein kinase, voltage-gated potassium channel, and nuclear hormone receptor), and 25 species (such as Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Sus scrofa, Rattus norvegicus, and Oryctolagus cuniculus) were included into our database, and all data were cross-linked to various well-established molecular biology databases.
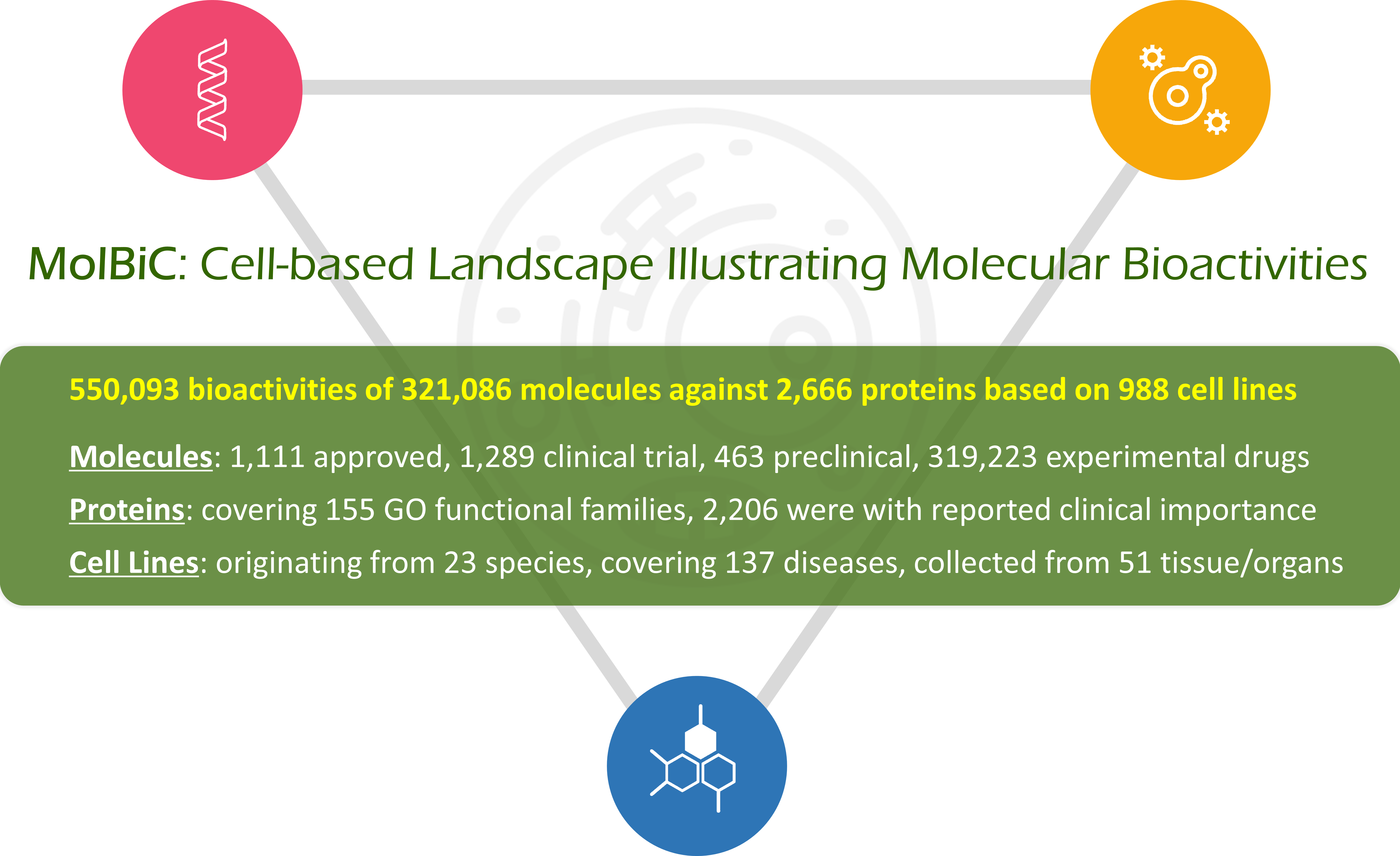
All in all, MolBiC was unique in providing the valuable data of cell-based molecular bioactivities (CMBs), which met the critical demands for CMB-based big data facilitating the learning of cell-based molecular/pharmaceutical patterns for guiding modern drug discovery. MolBiC is now freely accessible without any login requirement by all users.
MolBiC: a Cell-based Landscape Illustrating Molecular Bioactivities